Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yoshida, Naoki; Tashiro, Shinsuke; Amano, Yuki; Yoshida, Kazuo; Yamane, Yuichi; Abe, Hitoshi
NEA/CSNI/R(2017)12/ADD1 (Internet), p.293 - 305, 2018/01
The "Evaporation to Dryness due to the Loss of Cooling Functions" (EDLCF) of highly-active liquid waste (HALW) was newly defined as one of the severe accidents in Japan's nuclear safety standard for the reprocessing plant. Studies on accident scenarios and their source terms have led to an increased need for the development of accident management measures and the assessment of their effectiveness. Previous studies have shown that ruthenium was released at a greater rate than other elements because it formed volatile species such as ruthenium tetroxide (RuO ). In addition, ruthenium isotopes,
). In addition, ruthenium isotopes, 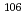 Ru and
Ru and 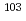 Ru, have radiotoxicity. Accordingly, the accident management measures require the experimental information on the release and transport behavior of the gaseous ruthenium (Ru(g)). This paper summarizes our experimental results on the characteristics of Ru(g) in the EDLCF. This work includes the results of the experiments carried out under the agreement among JAEA, Japan Nuclear Fuel Ltd. and Japan Nuclear Energy Safety Organization.
Ru, have radiotoxicity. Accordingly, the accident management measures require the experimental information on the release and transport behavior of the gaseous ruthenium (Ru(g)). This paper summarizes our experimental results on the characteristics of Ru(g) in the EDLCF. This work includes the results of the experiments carried out under the agreement among JAEA, Japan Nuclear Fuel Ltd. and Japan Nuclear Energy Safety Organization.
Yamane, Yuichi; Abe, Hitoshi
no journal, ,
After the experience of the accident at the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plants of Tokyo Electric Power Company (TEPCO),Japan's nuclear safety standard for reprocessing plant has been renewed and the standard now requires accident management measures and the assessment of their effectiveness to the severe accident such as criticality accident. This paper summarizes the issues for the best estimation in criticality accident consequence analysis and proposes a new method to estimate source term in criticality accident. Unique characters of criticality accident in nuclear fuel facilities, such as the production of short life nuclides, are described in association with the best estimation of public and worker's dose. In the light of those characters, this paper proposes a procedure to estimate source term in criticality accident by utilizing five-component equation described in DOE handbook.